The Stereo 3D on Future Drones
Note
This is one of my Masters assignment from Media Information Processing Course which has never been published anywhere and I, as the author and copyright holder, license this assignment customized CC-BY-SA where anyone can share, copy, republish, and sell on condition to state my name as the author and notify that the original and open version available here.
1. Stereoscopic 3D 2 camera
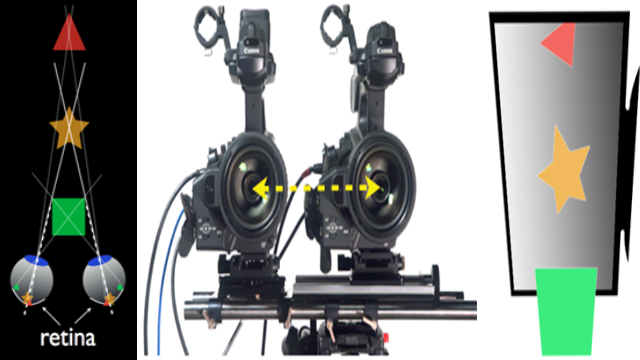
The first section explanation is from [1]. The stereoscopic 3D is a method to make 3D visual representation on an image using 2 camera’s. Stereo refers to “2” and 3D is 3 dimension. The concept is based on how our eyes perceives the visual aspect of the world as in Figure 1. We can just implement it at first is we create an image using digital camera, next video representation is possible as long as the method remains implemented. The result will be as Figure 2 where the top is the 2 image and the bottom is how we will perceive it.
There are few terms that might be unfamiliar to our ears. There is interocular separation which is the distance between the centers of the human eye, that is around 65mm for male adults. The interaxial separation is the distance between the 2 lenses of the camera. It’s not recommended to regard interaxial separation the same as interocular separation but interocular separation is used to calculate interaxial separation.

Figure 1. How our eye’s see and how to implement
If we return to Figure 1 we see that we are using binocular vision (“bi” means two) where we are using two eyes on our vision system. For us and other mammals commonly we use it to see how the depth of an object, how deep the object went, or how far the object is. When we look at an object from a distance the image projected will be located at slightly different location for our 2 retinas and our brain interpret this as retinal disparity. The same thing will happen if we use the two camera’s where the image will be registered in slightly different horizontal position which is called parallax. Another thing we can see on the first Figure is eyes are convergence when we focus on a certain object, the more closer the object to focus the more convergence (Figure 1 shows convergence eyes). Instead if the object goes further our eyes will tend to more divergence. For example when we focus on a cup we’ll see one image of the cup (actually it’s two image but we perceive as one image) and we focus the wall behind it instead we’ll see two cups.
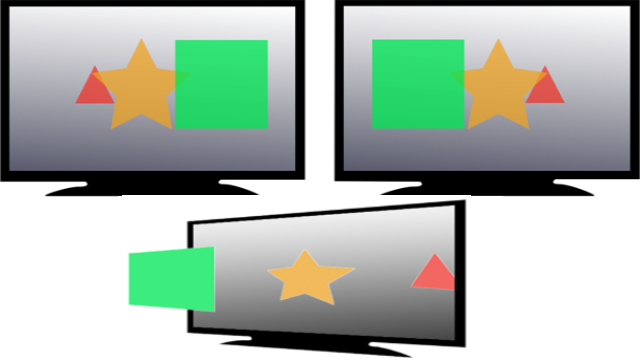
Figure 2. Preception in Stereo3D
In Figure 2 is just an illustration of how we emulate a binocular vision on a screen. We will perceive either it as positive parallax which is the red triangle appeared to be behind the window or negative parallax, the green square seems to be in front of the windows. Our brains perceive it that way and some may call it an illusion.
2. Stereoscopic 3D 1 camera
Still to produce this is by using 2 image that fulfills the requirement. Just one camera is possible to do this like on Figure 3 a person takes two pictures. [2]

Figure 3. Using one camera
When using a drone we simply have to apply a control system so the drone will capture 2 image separately that fulfills the requirement. A control system may be apply to compute the distance of where to take the left image and the right image. Compute the distance to the object, then find the left image and right image angle and distance.

Figure 4. Camera equipped with mirror
For video more complex method is needed. There is one on [3] that claims it’s possible using mirrors and prisms as on Figure 4. Another method is to use progressive image capturing where the camera shifts left and right [4]. It quickly captures image when shift to left and shift to right, the shifting process itself is very quick. An enhanced method is use a high frequency shifting while video recording example on Figure 5 [5]. The video is then process to cancel the vibration and shaking [6].

Figure 5. Camera on drown shifts left and right
3. Reference
- http://www.dashwood3d.com/blog/beginners-guide-to-shooting-stereoscopic-3d/
- https://adcnj3d.wordpress.com/shooting-3d-with-one-camera/
- https://www.lhup.edu/~dsimanek/3d/stereo/3dgallery16.htm
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stereo_camera#Types_of_stereo_cameras
- http://www.stereofpv.com/
- https://helpx.adobe.com/photoshop/using/reduce-camera-shake-induced-blurring.html
Mirrors
- https://www.publish0x.com/fajar-purnama-academics/the-stereo-3d-on-future-drones-xgpqqrg?a=4oeEw0Yb0B&tid=github
- https://0darkking0.blogspot.com/2021/02/the-stereo-3d-on-future-drones.html
- https://0fajarpurnama0.medium.com/the-stereo-3d-on-future-drones-f459ce652474
- https://0fajarpurnama0.github.io/masters/2020/07/23/stereo-3d-future-drones
- https://hicc.cs.kumamoto-u.ac.jp/~fajar/masters/stereo-3d-future-drones
- https://0fajarpurnama0.wixsite.com/0fajarpurnama0/post/the-stereo-3d-on-future-drones
- http://0fajarpurnama0.weebly.com/blog/the-stereo-3d-on-future-drones
- https://0fajarpurnama0.cloudaccess.host/index.php/9-fajar-purnama-academics/212-the-stereo-3d-on-future-drones
- https://read.cash/@FajarPurnama/the-stereo-3d-on-future-drones-8e0c367d
- https://www.uptrennd.com/post-detail/the-stereo-3d-on-future-drones~ODY0NzI1