College Assignment About Oscilloscope
Note
This is my undergraduate assignment that I translated to English myself in the Electrical Measurement course where the task is to write an essay on Oscilloscopes. This assignment has never been published anywhere and I, as the author and copyright holder, license this assignment customized CC-BY-SA where anyone can share, copy, republish, and sell on condition to state my name as the author and notify that the original and open version available here.
Chapter 1 Introduction
1.1 Background
Have you ever seen a line drawing that goes up and down, up and down again? Have you ever heard of signals, waves, vibrations, alternating current (AC)? Maybe on television you have seen the form of a signal displayed by news or educational media. Maybe you don’t know the measuring instrument that can display the wave image. The measuring instrument is called an oscilloscope.
1.2 Objective
- Know the term Oscilloscope.
- Know the basic circuit of the Oscilloscope.
- Identifying the outside (buttons) of the Oscilloscope.
- Know the basic ways of using the Oscilloscope.
- Get to know the various uses of the Oscilloscope.
1.3 Scope of Material
- Understanding oscilloscope.
- Basic oscilloscope diagram.
- Buttons on the Oscilloscope.
- An introduction to measurements on an oscilloscope.
- Oscilloscope applications in the outside world.
Chapter 2 Basic Theory
2.1 Vibration
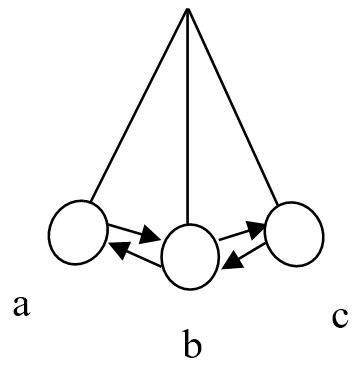
The vibrations can be in the form of up and down, left-right, left side - right side, back and forth. In life we feel vibrations are a continuous back and forth motion, for example earthquakes.
Movement of the pendulum from a to c back again to a or a > b > c > b > a is said to be 1 vibration.
2.2 Frequency
Frequency is defined as the number of vibrations that are carried out every second. The unit of frequency in the International System is hertz, abbreviated as Hz. This name is taken from the last name from the figure of Physics, whose name is Heinrich Hertz.
hertz = vibration/second, frequency = vibration/time
2.3 Period
Period is the time it takes to perform 1 vibration.
f swing takes 1 second,
2f swing takes 2 seconds,
100f swing takes 100 seconds,
f/2 swings take 1/2 second,
f/100 swings take 1/100 of a second,
f/f=1 swing, takes 1/f second,
T = 1/f
2.4 Wave
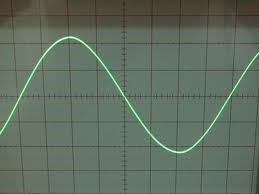
Waves are described as vibrations up and down.
Chapter 3 Discussion
3.1 What is an oscilloscope?
An oscilloscope is an electronic device that can provide an image on the screen (display) of the electrical signal connected to its input. Oscilloscopes usually have an input signal gate and an output signal. Oscilloscopes generally display images in 2 dimensions, the screen is in boxes. There are also 3 dimensions. A wave is converted into electricity, after which it can be read on an oscilloscope. With an oscilloscope it is possible to see the shape of the wave equation of an electrical signal.
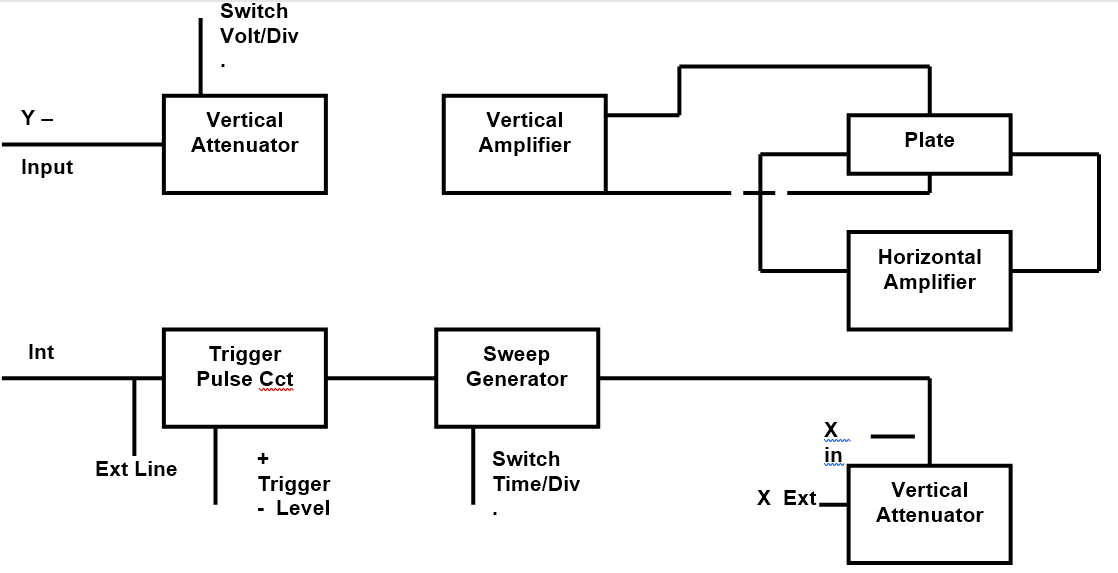
3.2 How is the basic circuit of an oscilloscope?
Oscilloscope Circuit
3.3 Name the buttons on the Oscilloscope?

The external physical parts of the oscilloscope.
- Circle 1 represents the signal source (CH1, CH2, LINE, and EXT).
- Circle 2 represents Channel 1 input.
- Circle 3 indicates which channel is displayed on the screen (CH1, CH2, DUAL, and ADD).
- Circle 4 represents the input signal type (AC, GND, and DC).
- Circle 5 represents Volts/Div.
- Circle 6 indicates Vertical Position.
- Circle 7 represents Horizontal Position.
- Circle 8 represents Time/Div (time per square on the oscilloscope screen).
- Grid screen (boxes), the lines of the squares, either horizontal or vertical, are called divs.
3.4 How to basically use it?
An explanation for the schematic of the analog oscilloscope working principle:
- When we connect a probe to a circuit, a voltage signal flows from the probe to the vertical arrangement of an oscilloscope system (Vertical System), an Attenuator will attenuate the input voltage signal while the Amplifier will amplify the input voltage signal. This setting is determined by us when moving the “Volt/Div” knob on the Oscilloscope user interface.
- The voltage that comes out of the vertical system is then forwarded to the vertical deflection plate on a CRT (Catode Ray Tube), the voltage signal that is inserted into this plate will later be used by the CRT to move the electron beams in a vertical plane only (up or down).
- Up to this point, it can be concluded that the Vertical System on an analog oscilloscope functions to adjust the amplitude appearance of the observed signal.
- Then the signal enters the vertical deflection plate. The voltage signal applied here causes the electron beams to move. A positive voltage causes the electron beam to move upwards, while a negative voltage causes the electrons to be pushed down.
- The signal that comes out of the Vertical System is also directed to the Trigger System to trigger the sweep generator to create what is called a “Horizontal Sweep”, namely the movement of electrons in a sweep - sweeping left and right - in a horizontal dimension or in other words, an expression for the action that causes electrons to move very quickly across the screen in a certain time interval. The movement of electrons is very fast (can reach 500,000 times per second) which causes the electrons to appear as lines on the screen (for example, like a fan on a fan that looks like a circle when it rotates).
- This setting of the number of times the electrons move across the screen is what we can think of as the Period/Frequency setting that appears on the screen, the concrete form is when we move the Time/Div knob on the Oscilloscope.
- Arrangement of the vertical and horizontal planes together finally can represent the observed voltage signal in the form of a graph that we can see on the CRT screen.
3.5 How is the application of the oscilloscope?
Some of the oscilloscope functions include::
- Measure the amount of voltage and its relationship to time.
- Measures the frequency of the oscillating signal.
- Checks the path of a signal on an electrical circuit.
- Differentiate between AC and DC currents.
- Determines the noise in an electrical circuit.
- Used in the engineering industry.
- Used in the scientific field.
- Used in the telecommunications sector.
Chapter 4 Closing
4.1 Conclusion
An oscilloscope is a device that displays electrical signals in the form of waves. Oscilloscopes are used in various fields. Provided that something can be defined in the form of waves.
4.2 Literature Review
- http://www.sisilain.net/2010/10/pengertian-osiloskop.html
- http://joe-proudly-present.blogspot.com/2010/11/osiloskop-analog.html
- http://www.sentra-edukasi.com/2009/06/materi-elektro-osiloskop-oscilloscope.html
- http://web.ipb.ac.id/~henrymanik/pdf/Tutorial%20OSILOSKOP.pdf
- Getaran dan Gelombang, 2009, Prof. Yohanes Surya, Ph.D
- MODUL PRAKTIKUM PENGUKURAN LISTRIK TEKNIK ELEKTRO UNIVERSITAS UDAYANA
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oscilloscope
Mirror
- https://www.publish0x.com/fajar-purnama-academics/college-assignment-about-oscilloscope-xpnneyw?a=4oeEw0Yb0B&tid=github
- https://0fajarpurnama0.github.io/bachelor/2020/08/06/oscilloscope-college-assignment
- https://0fajarpurnama0.medium.com/college-assignment-about-oscilloscope-efc15688702c
- https://hicc.cs.kumamoto-u.ac.jp/~fajar/bachelor/oscilloscope-college-assignment
- https://blurt.buzz/@fajar.purnama/college-assignment-about-oscilloscope?referral=fajar.purnama
- https://0darkking0.blogspot.com/2020/12/college-assignment-about-oscilloscope.html
- https://stemgeeks.net/technology/@fajar.purnama/college-assignment-about-oscilloscope?referral=fajar.purnama
- https://0fajarpurnama0.cloudaccess.host/index.php/9-fajar-purnama-academics/165-college-assignment-about-oscilloscope
- https://steemit.com/technology/@fajar.purnama/college-assignment-about-oscilloscope?r=fajar.purnama
- http://0fajarpurnama0.weebly.com/blog/college-assignment-about-oscilloscope
- https://0fajarpurnama0.wixsite.com/0fajarpurnama0/post/college-assignment-about-oscilloscope
- https://read.cash/@FajarPurnama/college-assignment-about-oscilloscope-9d9af1ab
- https://www.uptrennd.com/post-detail/college-assignment-about-oscilloscope~ODQxMjc1