Manually Set IP Address Version 4
Utility
Today, Internet Protocol (IP) address version 4 is majorly used between computer communication over the network. However, most common people does not know that IP address is set on the network interface and not in the core system of the computer. For example, a laptop can have two IP address, one is on the cable and one is on the WiFi. This article guides users in setting IP address manually which can be for:
- The network that we connect to have technical problem that we may have to set manually.
- The usual automatic IP address received maybe blacklist and may not be from the main system but from malicious peers such as those who uses netcut to monopolize the traffic.
- If you are going to be a administrator, you need to have this skill.
- If you are studying in computers and engineerings, you may stumble on a class that requires you to set IP address manually for an experiment.
- Eventhough you are not in computers or engineerings but you may come across a software that requires manual IP address setting.
Short Description
- IP address is the address of your network card and if you do not understand them well, just change the last numbers and if you do not have a reference for users, just set it to automatic, take note of the IP address you receive and set it manually to a similar number.
- Subnet mask determines the cluster of network you belong to. For example 192.168.1.2 with subnet mask 255.255.255.0 means you belong to a cluster which groups IP address ranging 192.168.1.0 - 192.168.1.255.
- Gateway is the IP address destination when you want to send packet outside of the network. For example, to the Internet, if you cannot connect to the Internet, most likely a proble with your gateway configuration or the gateway itself.
- Domain Name Service (DNS) is a server destination that can understand domain names. Your browser will not understand www.google.com without a DNS server. If you successfully connect to the Internet but cannot open any website, then DNS setting can potentially be the problem.
- Gateway metric is rarely touch because this configuration is only necessary if you more than one gateway for example you connect to the Internet using two different network such as cable and wireless. Without any settings, your computer will be confused so set the metric with a number. A metric with higher number will have lower priority and vice versa.
- Learn more about the fundamental at Introduction to Simple Computer Network.
Set Up IP Address Manually
Windows GUI
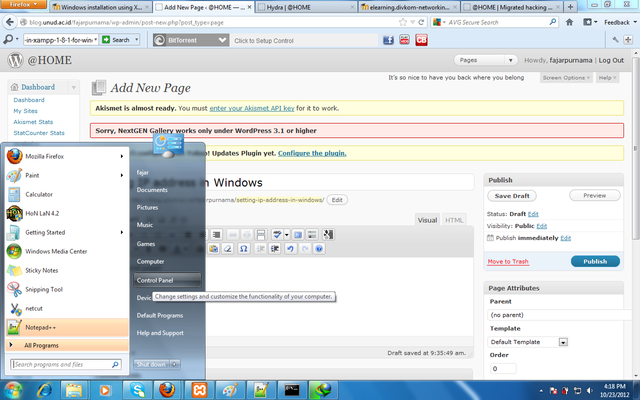
Go to control panel.
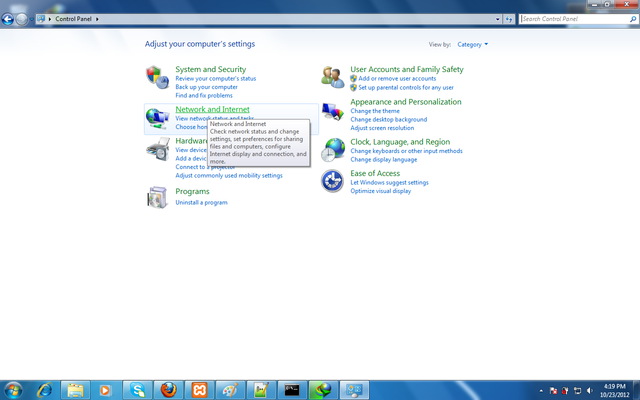
Click Network and Internet.
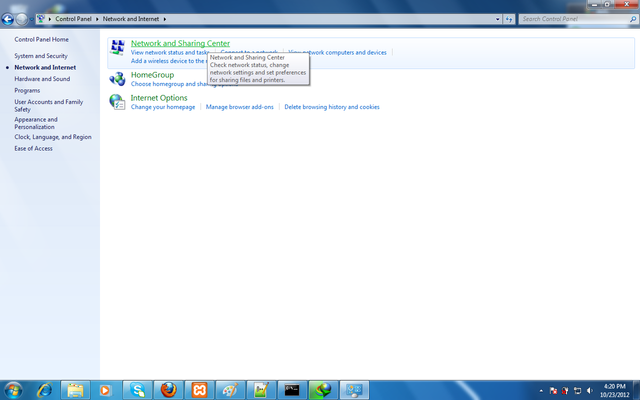
Click Network and Sharing Center.
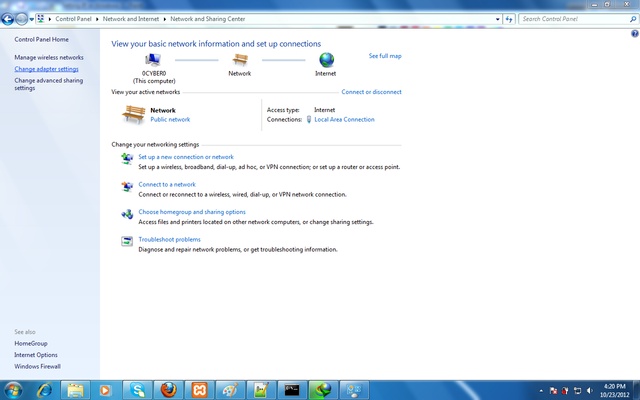
Change Adapter Setting.
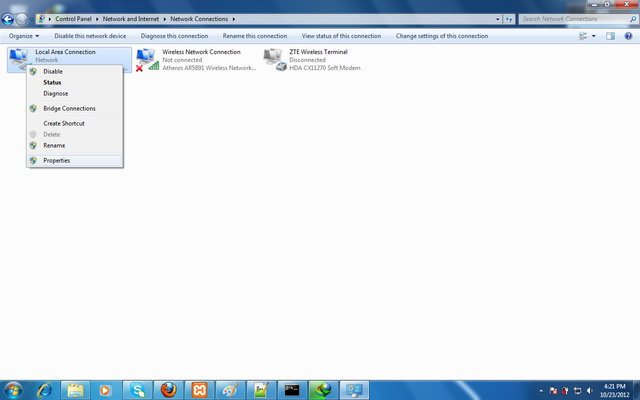
Choose a connection, right click, and properties.
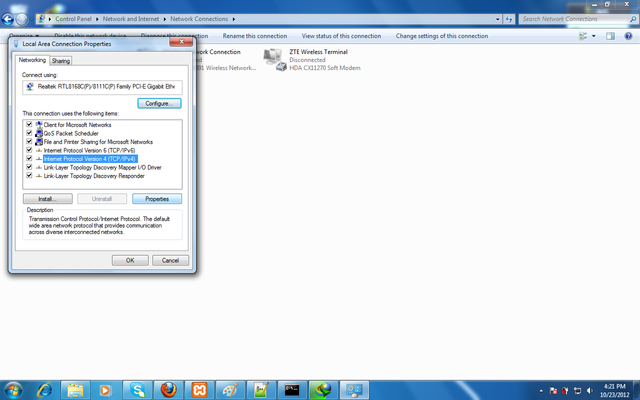
Open Internet Protocol.
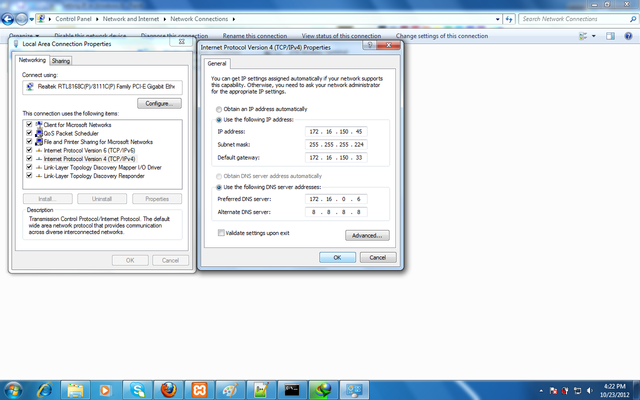
Use Following.
Windows Command Line
Using command prompt (CMD):
netsh interface show interface netsh interface ip set address "[chosen interface]" static [ip address] [subnet mask] [gateway] [metric] netsh interface ipv4 set dns name=”[YOUR INTERFACE NAM]” static [DNS SERVER], for example: netsh interface ip set address "Ethernet" static 192.168.100.25 255.255.255.0 192.168.100.1 1 netsh interface ipv4 set dns name=”8.8.8.8” static Ethernet
Linux GUI (Debian)

Go to settings or straight to network manager.
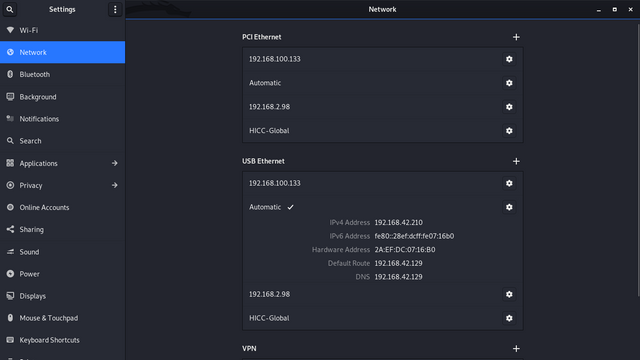
Go to WiFi or Network.
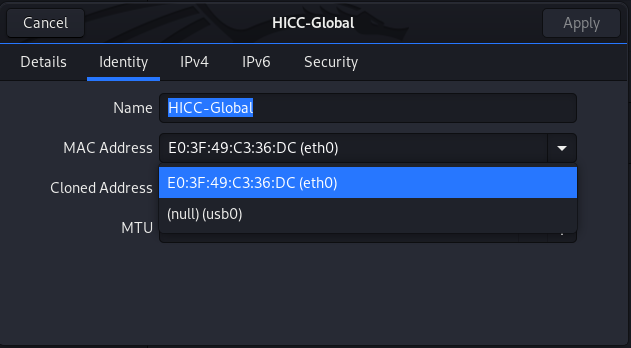
Go to Identity and Choose a Network Interface.
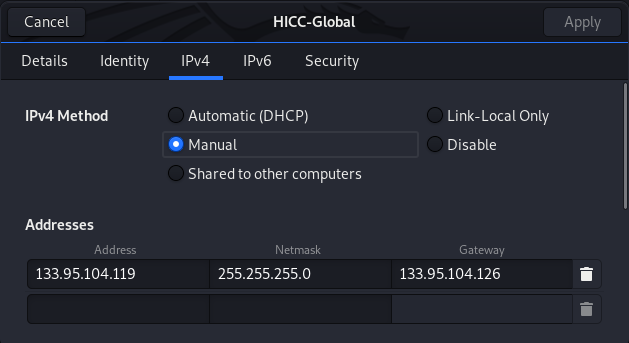
Go to IP, choose manual, and input addresses.
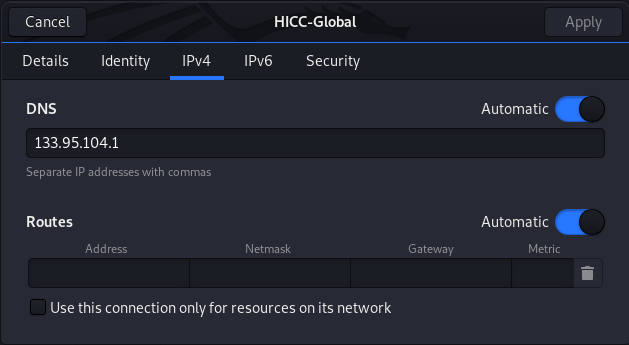
Scroll down and set DNS also routes if necessary.
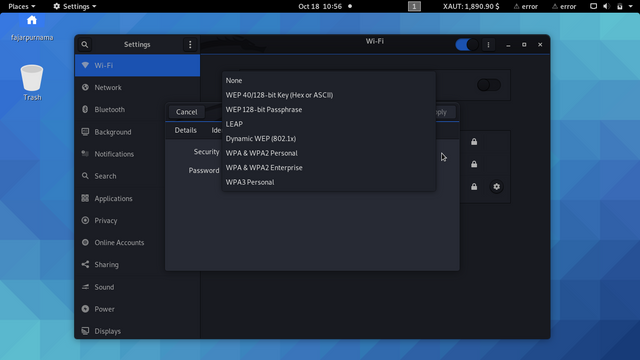
If necessary, go to security.
Linux Command Line (Debian)
Using ifconfig:
sudo ifconfig [interface] [ip address] netmask [subnet mask] up route add default gw [IP-ADDRESS] [INTERFACE-NAME], for example sudo ifconfig eth0 192.168.100.22 netmask 255.255.255.0 up route add default gw 192.168.100.1 eth0
Using ip:
sudo ip addr add [ip address]/[netmask id] dev [interface] sudo ip route add default via [gateway], for example sudo ip addr add 192.168.100.22/24 dev eth0 sudo ip route add default via 192.168.100.1
For DNS, edit /etc/resolve.conf:
nameserver 8.8.8.8
Mirrors
- https://www.publish0x.com/0fajarpurnama0/manually-set-ip-address-version-4-xllrnxe?a=4oeEw0Yb0B&tid=github
- https://0darkking0.blogspot.com/2020/10/manually-set-ip-address-version-4.html
- https://medium.com/@0fajarpurnama0/manually-set-ip-address-version-4-72cb061877c5
- https://0fajarpurnama0.github.io/internet/2020/10/18/manually-set-ip-address-version-4
- https://blurt.world/blurtech/@fajar.purnama/manually-set-ip-address-version-4?r=fajar.purnama
- https://hive.blog/computers/@fajar.purnama/manually-set-ip-address-version-4?r=fajar.purnama
- https://steemit.com/computers/@fajar.purnama/manually-set-ip-address-version-4?r=fajar.purnama
- https://hicc.cs.kumamoto-u.ac.jp/~fajar/internet/manually-set-ip-address-version-4.html
- https://0fajarpurnama0.wixsite.com/0fajarpurnama0/post/manually-set-ip-address-version-4
- http://0fajarpurnama0.weebly.com/blog/manually-set-ip-address-version-4
- https://0fajarpurnama0.cloudaccess.host/index.php/uncategorised/75-manually-set-ip-address-version-4
- https://read.cash/@FajarPurnama/manually-set-ip-address-version-4-aa00e5c1
- https://www.uptrennd.com/post-detail/manually-set-ip-address-version-4~Nzc2OTI3