Intrusion Detection System Important Specifications
The performance of an intrusion detection system (IDS) is how well an IDS can detect intrusions in a given network. There are many factors in measuring its performance, but in my opinion a good IDS can detect a variety of attacks, can function on a high traffic, and doesn’t greatly decrease the working performance of the users. It ceases to function as an IDS if it cannot detect, no use if it can’t handle high traffic, and a bother if it just keeps disturbing the users. This is the sixth assignment from my Masters Advanced Network Security Course which has never been published anywhere and I, as the author and copyright holder, license this assignment customized CC-BY-SA where anyone can share, copy, republish, and sell on condition to state my name as the author and notify that the original and open version available here.
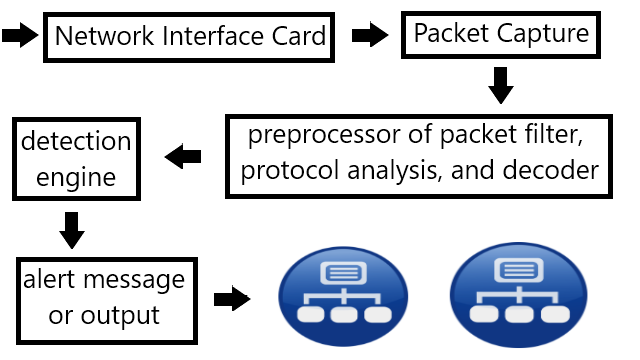
That’s the simple explanation regarding to the IDS but still lots left uncover. To start investigating the performance of an IDS we can first look at the structure of and IDS. For example open source IDS Snort consists of (1) network interface card, (2) packet capture, (3) preprocessor of packet filter, protocol analysis, and decoder, (4) detection engine, and (5) alert message or output. (1) determines how much packet it could receive, (2) and (3) are essential to capture and identify the packets, and (4) itself is the heart of the IDS which determines whether the packet is a threat or not, lastly (5) informs the administrators. When packets goes through (1), (2) (3) and (4) process the packets thus a performance can be measured seeing how much packet it could process, how are dropped, in special cases how much slips the inspection. With these IDS structure many have identified factors that determines the performance if IDS.
- Coverage, is a parameter of how many kinds of attacks it could identify in an ideal environment (theoretically). For signature based IDS is how much attack patterns recorded on the database and for anomaly based IDS is based on the defined ideal networking of the protocol and the traffic.
- Detection capability, a measurement of how well it could detect on certain network configuration and traffic. The deeper the analysis the better that contains the severity of the attack and the outcome attack was successful or not. Even further it could detect unknown attacks.
- Processing power, which determines how much load it could take. We can improve the hardware, configure the network (the network topology, where the NIDS should be placed or how it should be configured when on a bus network or using layer 2 switch, which should be installed an HIDS), or the mechanism of the analyzer (core of the IDS) for example the developing a better search algorithm on the detection engine.
- False negative, which is a parameter of undetected threats passed. A signature-based IDS tends to have higher false negative because in can only detect threats that are recorded on the database, and cannot cope with unknown attacks. Different from anomaly-based IDS which detects the abnormality on the network whether it is protocol abnormality (example dropping packets requesting SSH on other than port 22) or traffic abnormality (example high traffic on port SMTP).
- False positive, is equivalent to false alarm where the IDS alerts when it’s not actually a threat. Anomaly-based IDS tends to succumb more to this factor since it detects by abnormality in traffic, when the traffic on that day is actually high. Signature-based IDS is more accurate because it is specialized on the attack itself. With so many false positive could also annoys the administrators and instead could miss out on the alerts when it’s a real positive.
A good IDS should have wide coverage, high detection capability and processing power, and low false negative and positive. The factors above are still the surfaces, and there’s still more deeper such as stability, sustainability, resistance to attacks on IDS itself, ability to correlate event, ability to handle high bandwidth traffic, capacity verification, etc.
Mirrors
- https://www.publish0x.com/fajar-purnama-academics/intrusion-detection-system-important-specifications-xgpvxvl?a=4oeEw0Yb0B&tid=github
- https://0darkking0.blogspot.com/2021/02/intrusion-detection-system-important.html
- https://0fajarpurnama0.medium.com/intrusion-detection-system-important-specifications-e0cfced5aed7
- https://0fajarpurnama0.github.io/masters/2020/07/11/intrusion-detection-system-important-specifications
- https://hicc.cs.kumamoto-u.ac.jp/~fajar/masters/intrusion-detection-system-despite-antivirus-firewall
- https://steemit.com/technology/@fajar.purnama/intrusion-detection-system-important-specifications?r=fajar.purnama
- https://stemgeeks.net/technology/@fajar.purnama/intrusion-detection-system-important-specifications?ref=fajar.purnama
- https://blurtter.com/blurtech/@fajar.purnama/intrusion-detection-system-important-specifications?referral=fajar.purnama
- https://0fajarpurnama0.wixsite.com/0fajarpurnama0/post/intrusion-detection-system-important-specifications
- http://0fajarpurnama0.weebly.com/blog/intrusion-detection-system-important-specifications
- https://0fajarpurnama0.cloudaccess.host/index.php/9-fajar-purnama-academics/196-intrusion-detection-system-important-specifications
- https://read.cash/@FajarPurnama/intrusion-detection-system-important-specifications-5befebab
- https://www.uptrennd.com/post-detail/intrusion-detection-system-important-specifications~ODU4NTM4